Prefabricated Homes – Affordable and Efficient Housing Options with Fast Installation
Prefabricated homes represent a revolutionary approach to residential construction, offering homeowners a faster, more cost-effective alternative to traditional building methods. These factory-built structures combine quality craftsmanship with streamlined production processes, delivering complete housing solutions that can be assembled on-site in a fraction of the time required for conventional construction.
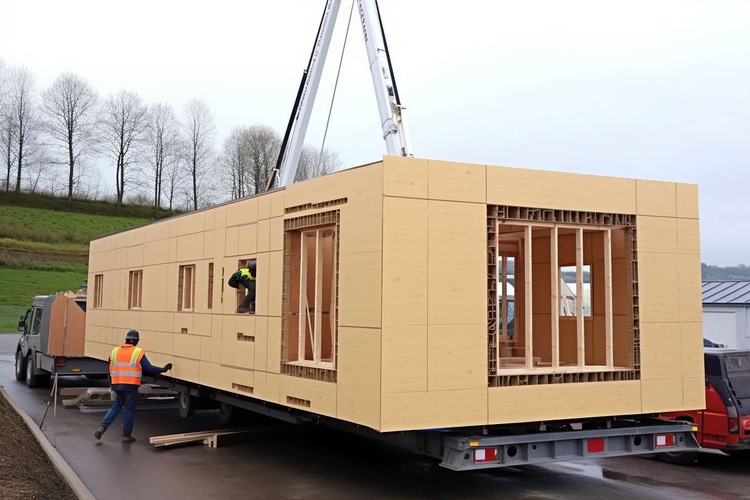

The Canadian housing market has witnessed a growing interest in alternative construction methods, with prefabricated homes emerging as a practical solution for those seeking efficient, quality housing. This construction approach combines modern manufacturing techniques with traditional homebuilding principles to deliver homes that meet contemporary living standards while addressing common construction challenges.
What Are Prefabricated Homes and How Do They Work?
Prefabricated homes are residential structures manufactured in controlled factory environments before being transported and assembled at their final location. The process begins with detailed architectural planning, followed by precision manufacturing of wall panels, roof trusses, and other structural components. Factory workers construct these elements using standardized processes that ensure consistent quality and dimensional accuracy.
The manufacturing environment provides several advantages over traditional on-site construction. Climate-controlled facilities eliminate weather-related delays, while specialized equipment and assembly lines enable efficient production. Quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process help identify and address issues before components reach the building site.
How Do Efficient Prefabricated Homes Compare to Traditional Construction?
Prefabricated construction offers distinct advantages in terms of timeline and resource efficiency. Traditional stick-built homes typically require several months of on-site construction, weather permitting, while prefabricated homes can often be assembled within days or weeks once foundation work is complete.
Energy efficiency represents another key comparison point. Factory-built components often achieve superior insulation performance due to precise manufacturing tolerances and controlled assembly conditions. Many prefabricated homes incorporate advanced building envelope technologies that exceed standard building code requirements for thermal performance.
Waste reduction also favors prefabricated construction. Factory environments enable precise material calculations and efficient use of lumber and other building materials, typically generating significantly less construction waste compared to traditional building sites.
What Types of Prefabricated Home Designs Are Available?
The prefabricated housing market offers diverse design options to suit various lifestyle preferences and site conditions. Modular homes represent the most comprehensive approach, featuring complete room modules that are transported and connected on-site. These homes can range from simple single-story designs to complex multi-level configurations.
Panel systems provide another popular option, where wall, floor, and roof panels are manufactured separately and assembled on-site. This approach offers greater design flexibility while maintaining manufacturing efficiency benefits.
Tiny homes and accessory dwelling units have gained popularity within the prefabricated market, offering compact living solutions for urban lots or as secondary housing options. These smaller structures often feature innovative space-saving designs and sustainable building technologies.
How Do Zoning Laws and Building Codes Affect Prefab Installation?
Canadian municipalities maintain specific regulations governing prefabricated home installation, with requirements varying significantly between provinces and local jurisdictions. Most prefabricated homes must comply with the same building codes as traditional construction, including structural, electrical, and plumbing standards.
Zoning regulations often address setback requirements, height restrictions, and architectural guidelines that can influence prefabricated home design and placement. Some communities have specific provisions for modular or manufactured housing, while others treat prefabricated homes identically to traditional construction.
Permitting processes typically require detailed plans and engineering specifications before approval. Homeowners should consult local building departments early in the planning process to understand specific requirements and potential restrictions that might affect their prefabricated home project.
Real-World Cost Insights for Prefabricated Homes
Prefabricated home costs in Canada vary significantly based on size, design complexity, and regional factors. Understanding typical pricing structures helps potential homeowners make informed decisions about this housing option.
| Home Type | Size Range | Cost Estimation (CAD) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Modular | 1,000-1,500 sq ft | $150,000-$250,000 | Standard finishes, simple layout |
| Custom Modular | 1,500-2,500 sq ft | $250,000-$400,000 | Upgraded finishes, complex design |
| Panel System | 1,200-2,000 sq ft | $180,000-$320,000 | Site-built assembly, flexible design |
| Tiny Home | 400-800 sq ft | $80,000-$150,000 | Compact design, efficient systems |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Additional costs beyond the base home price include site preparation, foundation work, utility connections, and transportation. Site preparation costs can range from $20,000 to $50,000 depending on soil conditions and accessibility. Foundation requirements typically add $15,000 to $30,000 to the total project cost.
Transportation expenses depend on distance from manufacturing facility to building site, with costs generally ranging from $5,000 to $15,000 for standard-sized modules. Crane services for module placement typically cost between $2,000 and $5,000 per day.
Prefabricated homes continue to evolve as a viable housing solution for Canadian families seeking efficient construction methods and predictable project timelines. While initial planning requires careful consideration of local regulations and site-specific factors, the controlled manufacturing environment and reduced construction time offer compelling advantages for many homebuilding projects. Success with prefabricated housing depends largely on thorough research, proper planning, and working with experienced manufacturers and local contractors familiar with modular construction techniques.