Prefabricated Homes – Affordable and Efficient Housing Options with Fast Installation
Prefabricated homes represent a revolutionary approach to residential construction, offering homeowners a faster, more cost-effective alternative to traditional building methods. These factory-built structures combine quality craftsmanship with streamlined production processes, delivering complete housing solutions that can be assembled on-site in a fraction of the time required for conventional construction.

The housing market has witnessed significant transformation in recent years, with prefabricated homes emerging as a viable solution to address affordability challenges and construction delays. These factory-built structures offer streamlined production processes and reduced waste, making them attractive to environmentally conscious buyers and those seeking faster move-in timelines.
What Defines Prefabricated Homes and Their Construction Process?
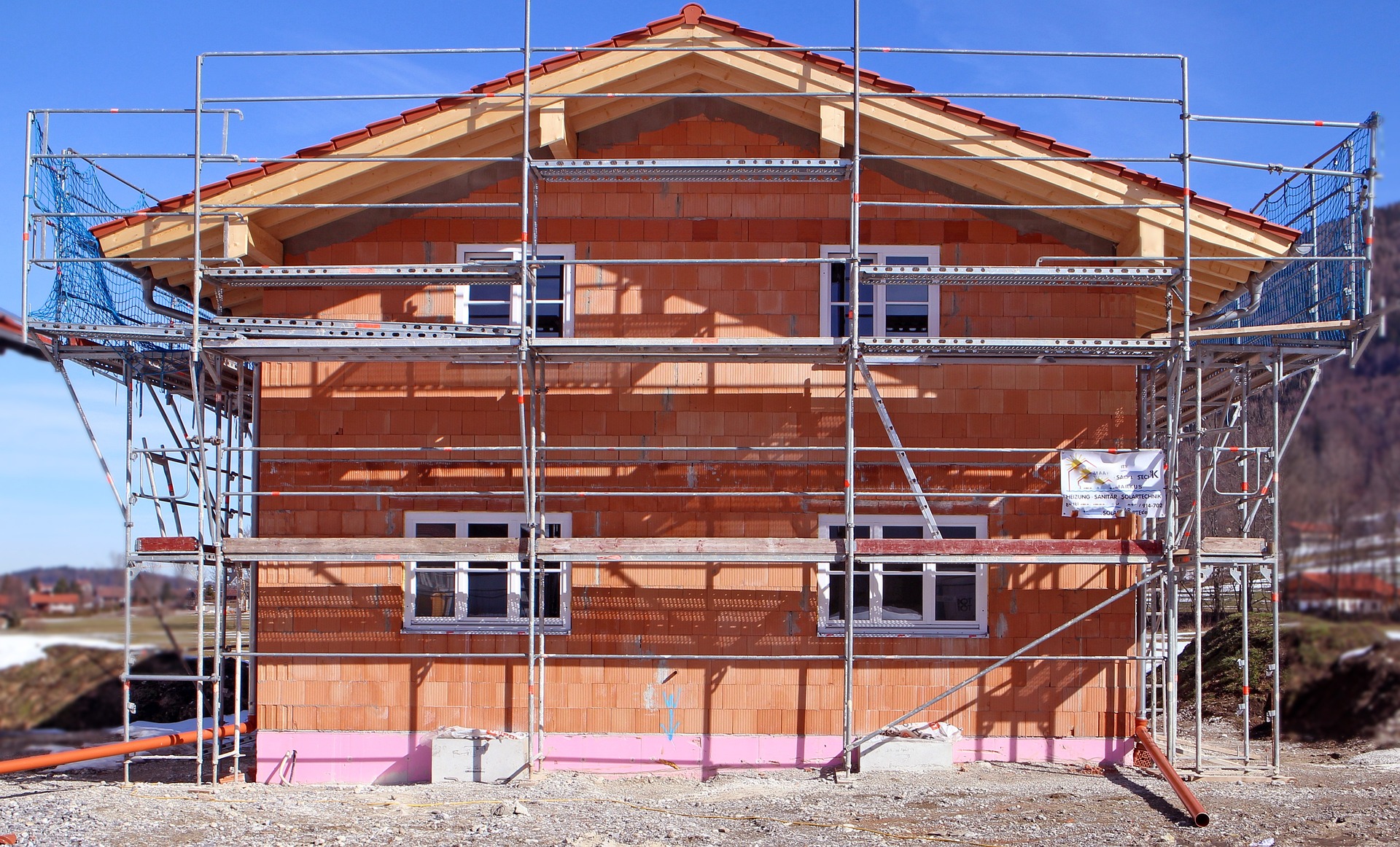
Prefabricated homes are residential structures manufactured in sections or modules within factory settings before being transported to their final locations. The construction process begins with architectural planning and design approval, followed by the fabrication of wall panels, floor systems, roof trusses, and other components in climate-controlled facilities. Workers assemble these elements using precision equipment and standardized procedures that ensure consistent quality control. Once completed, the sections are shipped to the building site where crews install them on prepared foundations. The entire process typically involves electrical, plumbing, and HVAC systems being integrated during factory production, reducing on-site labor requirements. Final assembly can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on the home’s size and complexity. This manufacturing approach minimizes weather-related delays and material waste compared to traditional stick-built construction.
Comparing Efficient Prefabricated Homes with Traditional Building Methods
When evaluating prefabricated homes against conventional construction, several factors distinguish the two approaches. Traditional site-built homes involve extensive on-location labor, with materials delivered and assembled piece by piece over several months. Weather conditions, labor shortages, and supply chain disruptions can significantly extend timelines. Prefabricated construction mitigates many of these challenges through controlled manufacturing environments and streamlined logistics. Material costs often prove lower due to bulk purchasing and reduced waste, while labor expenses decrease because factory workers complete most tasks before transportation. Energy efficiency tends to be higher in prefabricated homes due to tighter construction tolerances and modern insulation techniques applied during manufacturing. However, transportation costs and crane rental fees for assembly can offset some savings. Customization options may be more limited in prefabricated models compared to fully custom site-built homes, though this gap has narrowed as manufacturers expand their design catalogs.
Exploring Available Prefabricated Home Designs and Customization Options
The prefabricated housing industry offers diverse design options ranging from compact single-story cottages to expansive multi-level residences. Manufacturers typically provide base models that buyers can modify through various customization packages. Exterior finishes might include traditional siding, modern metal panels, or natural wood cladding, while interior layouts can be adjusted to accommodate different room configurations and family needs. Floor plans generally range from 600 to 3,000 square feet, with options for additional features such as garages, covered porches, and finished basements where site conditions permit. Some manufacturers specialize in contemporary minimalist designs, while others focus on traditional architectural styles that blend with established neighborhoods. Buyers can usually select flooring materials, cabinetry finishes, countertop surfaces, and fixture styles during the ordering process. Advanced manufacturers now offer virtual design tools that allow customers to visualize modifications before production begins. The degree of customization available depends on the manufacturer’s capabilities and the specific production system they employ.
| Home Type | Size Range | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Modular | 1,000-1,500 sq ft | $80,000-$150,000 |
| Standard Modular | 1,500-2,000 sq ft | $150,000-$220,000 |
| Premium Modular | 2,000-3,000 sq ft | $220,000-$350,000 |
| Panelized System | 1,200-2,500 sq ft | $100,000-$280,000 |
| Container-Based | 600-1,500 sq ft | $60,000-$180,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Understanding Zoning Laws and Building Codes for Prefabrication
Navigating regulatory requirements represents a critical aspect of prefabricated home installation. Local zoning ordinances determine where these structures can be placed, with some jurisdictions maintaining restrictions based on outdated perceptions of manufactured housing quality. Building codes at the federal, state, and local levels establish minimum construction standards that prefabricated homes must meet. The Department of Housing and Urban Development oversees manufactured homes built on permanent chassis, while modular and panelized homes typically fall under the same International Residential Code standards as site-built houses. Prospective buyers should verify that their chosen manufacturer produces homes certified for their specific location. Foundation requirements vary by region, with some areas mandating full basements while others permit slab or crawl space installations. Setback requirements, height restrictions, and architectural review board approvals may apply depending on the property’s location. Working with experienced local contractors familiar with prefabricated installation helps ensure compliance with all applicable regulations. Some municipalities have streamlined approval processes for certified prefabricated homes, recognizing their quality and safety standards.
Key Advantages of Prefabricated Homes in the Modern Housing Market
Prefabricated homes offer several compelling benefits that appeal to today’s homebuyers. Construction timelines typically range from three to six months from order to occupancy, compared to nine to twelve months for comparable site-built homes. This speed advantage proves particularly valuable in rapidly growing markets where housing demand exceeds supply. Cost predictability represents another significant benefit, as factory production reduces the budget overruns common in traditional construction projects. Environmental sustainability appeals to eco-conscious buyers, with prefabricated construction generating less waste and often incorporating energy-efficient materials and systems. Quality control processes in factory settings tend to produce more consistent results than on-site construction exposed to varying weather conditions and workforce skill levels. Financing options have expanded as lenders increasingly recognize prefabricated homes as permanent structures comparable to traditional houses. Resale values have improved as public perception shifts and more high-quality prefabricated homes enter the market. These advantages position prefabricated housing as a practical solution for first-time buyers, retirees seeking to downsize, and investors developing rental properties.
The growing acceptance of prefabricated homes reflects broader changes in construction technology and housing market dynamics. As manufacturing techniques advance and design options expand, these efficient building methods continue gaining market share. Buyers considering prefabricated options should research manufacturers thoroughly, understand local regulations, and work with experienced professionals to ensure successful project completion. The combination of affordability, speed, and quality makes prefabricated homes an increasingly relevant choice in the contemporary housing landscape.