Prefabricated Homes in US: 2026 Guide with Options and Pricing
Prefabricated homes, also known as prefab or modular homes, represent an increasingly popular housing solution in the United States. These structures are manufactured off-site in controlled factory environments and then assembled on the designated property. As we look toward 2026, prefabricated homes offer innovative design options, enhanced energy efficiency, and potentially significant cost savings compared to traditional construction methods.

Understanding Prefabricated Home Construction Methods
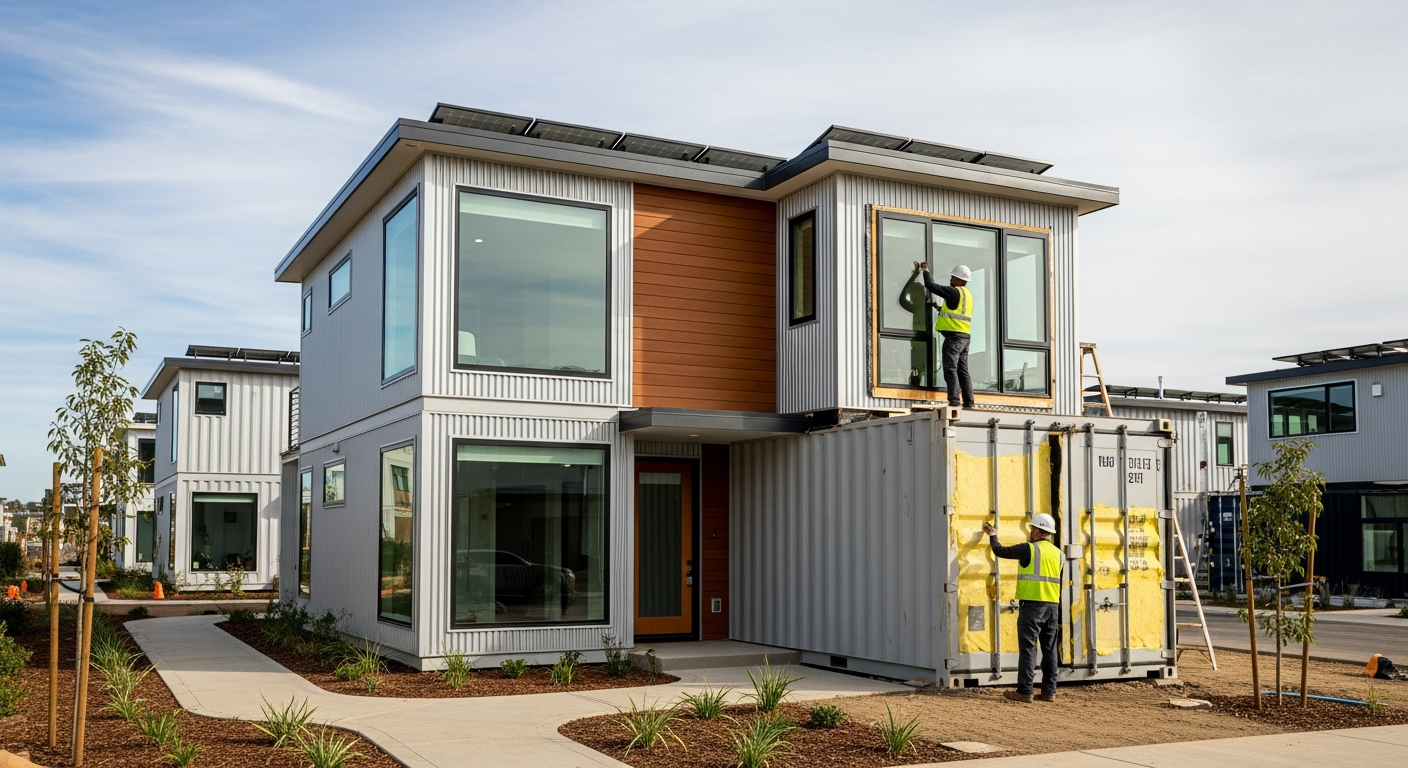
Prefabricated homes encompass several distinct construction methods, each with unique characteristics. Modular homes, for instance, are built in sections or modules in a climate-controlled factory, complete with plumbing, electrical, and interior finishes. These modules are then transported to the building site and assembled on a permanent foundation, adhering to local building codes just like site-built homes. Manufactured homes, often referred to as mobile homes, are also factory-built but are constructed on a non-removable steel chassis and meet federal HUD code standards. Panelized homes involve manufacturing wall, floor, and roof panels in a factory, which are then shipped to the site and erected. Kit homes, on the other hand, provide pre-cut materials and plans for assembly, often by the homeowner or a local builder. The core benefit across these methods is the controlled environment of factory production, which can lead to reduced waste, improved quality consistency, and protection from weather delays.
Current Market Trends for Prefabricated Homes in 2026
The landscape for prefabricated homes in the United States is continuously evolving, with several key trends shaping its trajectory towards 2026. A notable trend is the increasing demand for sustainable and energy-efficient designs. Many manufacturers are incorporating advanced insulation, renewable energy systems, and eco-friendly materials to meet environmental standards and consumer preferences. There is also a growing emphasis on smart home technology integration, allowing for automated climate control, security systems, and lighting. Furthermore, prefabricated homes are increasingly viewed as a viable solution to address housing shortages, particularly in areas experiencing rapid population growth. The market is also seeing a rise in more sophisticated and aesthetically diverse designs, moving beyond traditional perceptions to offer a wide range of architectural styles that appeal to a broader demographic.
Available Design Options and Customization Features
One common misconception about prefabricated homes is a lack of design variety; however, the reality is quite different. Today’s prefabricated market offers an extensive array of design options, ranging from sleek, modern minimalist structures to traditional ranch-style homes, and even multi-story residences. Homebuyers can often choose from a catalog of floor plans, which can then be customized to varying degrees. Customization features may include selecting exterior finishes such as siding, roofing materials, and window styles, as well as interior elements like cabinetry, flooring, countertops, and paint colors. Some manufacturers also offer options for adding garages, decks, or specific room configurations. While the level of customization can depend on the builder and the specific construction method, the flexibility available allows for a significant degree of personalization to suit individual tastes and needs.
Pricing Structure and Cost Considerations
The pricing of prefabricated homes is influenced by numerous factors, making a direct comparison to traditional homes complex. Generally, the base price of a prefabricated home covers the cost of the structure itself, built in the factory. However, several additional costs must be factored in to determine the total project expense. These often include land acquisition, site preparation (such as excavation, grading, and utility trenching), foundation work, transportation of the home modules or panels to the site, crane rental for assembly, utility hookups (water, sewer, electricity), permits, and any local service installation fees. The choice of materials, finishes, and the extent of customization also significantly impact the final price. While prefabricated homes can offer cost predictability due to streamlined production, it is crucial to account for all these variables during the budgeting phase.
Construction Timeline and Installation Process
The construction timeline for prefabricated homes typically offers a significant advantage over traditional site-built methods. The process begins with design finalization and permitting, followed by the factory production phase, which can often be completed in a matter of weeks or a few months, depending on the complexity and manufacturer’s schedule. Concurrently, site preparation, including foundation work and utility installation, takes place on the building lot. Once the factory-built components are ready, they are transported to the site. The installation process involves assembling the modules or panels onto the prepared foundation, which is often completed within days. After the structural assembly, the final finishing touches, such as connecting utilities, installing interior fixtures, and completing exterior landscaping, are carried out by local contractors. This parallel processing of factory construction and site work contributes to a generally faster overall project completion time compared to conventional building.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Small Manufactured Home (basic) | Clayton Homes | $60,000 - $120,000 (home only) |
| Mid-Range Modular Home (standard) | Nationwide Homes | $150,000 - $300,000 (home only) |
| Custom Modular Home (high-end) | Blu Homes | $300,000 - $700,000+ (home only) |
| Panelized Home (shell kit) | Method Homes | $70 - $150 per sq ft (for shell kit, without site work) |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Conclusion
Prefabricated homes present a compelling option for those seeking efficient, quality-controlled, and often more predictable housing solutions in the United States. With diverse construction methods, evolving market trends focusing on sustainability and technology, and a wide array of design possibilities, these homes are increasingly meeting the varied needs of modern homeowners. Understanding the full scope of costs, including both the factory-built component and site-specific expenses, is essential for a comprehensive financial plan. The streamlined construction and installation processes also offer a notable advantage in terms of project duration, making prefabricated homes a significant segment of the future housing landscape.