Understanding Affordable Energy-Efficient Prefabricated Homes in the US (2026)
Prefabricated homes in the United States combine factory-built components with on-site assembly to shorten construction timelines and reduce material waste. This article explains core concepts, installation processes, cost factors, energy performance, and environmental implications relevant to 2026.
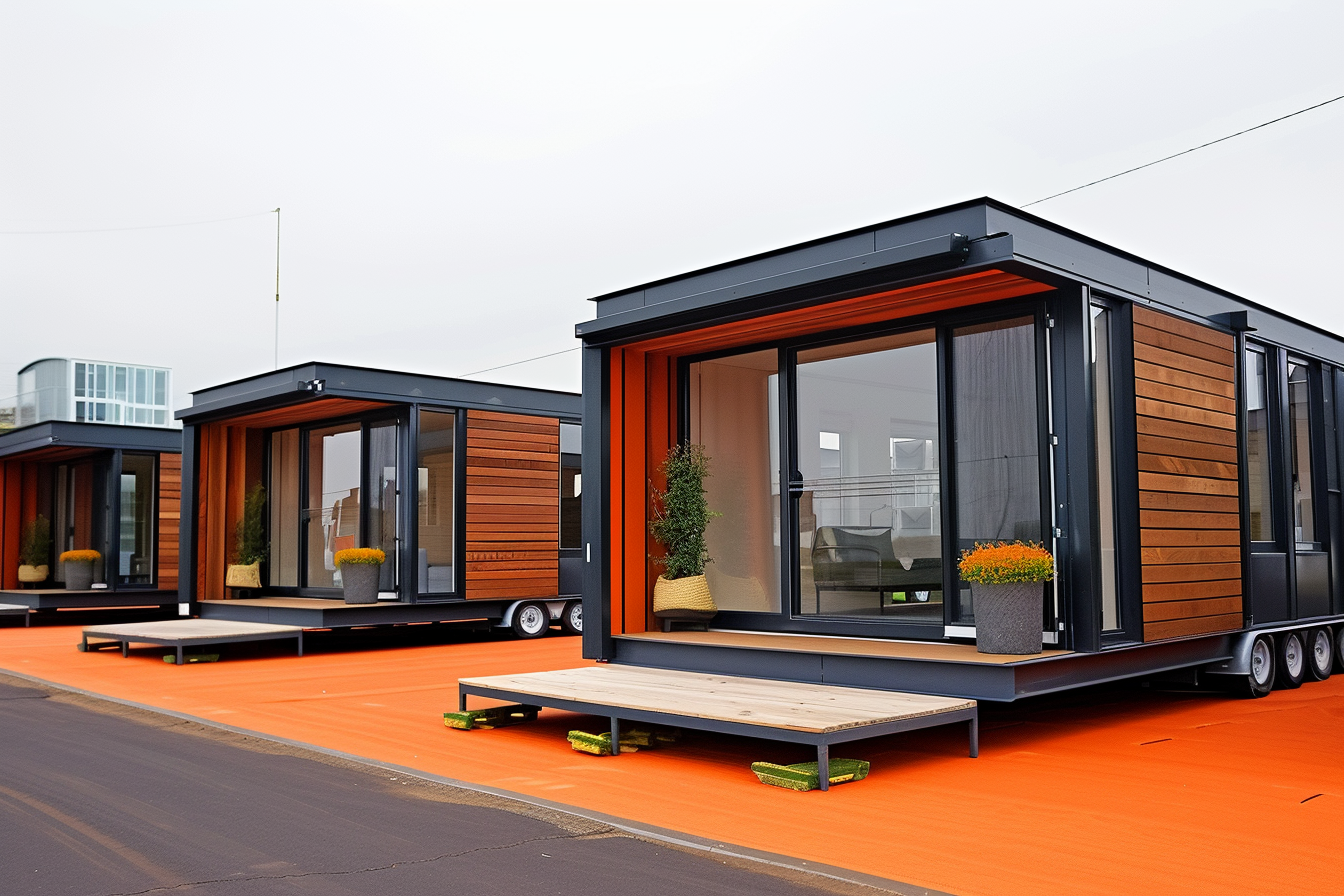

The housing market continues to evolve as buyers and builders seek innovative solutions that balance affordability, quality, and sustainability. Prefabricated homes have emerged as a compelling alternative to traditional stick-built construction, offering advantages that address many challenges facing today’s homebuyers. Understanding what makes these homes unique and how they deliver value can help prospective homeowners make informed decisions about their housing options.
What Are Prefabricated Homes and Why Are They Becoming More Popular?
Prefabricated homes are residential structures manufactured in factory settings before being transported to their final location for assembly. Unlike traditional homes built entirely on-site, prefab homes are constructed in controlled environments where weather delays and material theft are minimized. The factory setting allows for precise construction using standardized processes and quality control measures.
Several factors contribute to the growing popularity of prefabricated housing. Economic pressures including rising labor costs and material price fluctuations make the efficiency of factory production increasingly attractive. Additionally, younger homebuyers prioritize sustainability and modern design, both areas where prefab construction excels. The ability to customize floor plans while maintaining cost efficiency appeals to buyers seeking personalized homes without custom-build price tags. Housing shortages in many regions have also prompted builders and municipalities to embrace faster construction methods that can deliver homes more quickly.
The Process Behind Shorter On-Site Installation in Prefabricated Construction
The construction timeline for prefabricated homes differs significantly from traditional building methods. Factory production typically takes six to twelve weeks, during which walls, floors, roofing systems, and interior components are assembled in climate-controlled facilities. While manufacturing occurs, site preparation including foundation work proceeds simultaneously, reducing overall project duration.
Once modules or panels arrive at the building site, installation can be completed in days or weeks rather than months. Crews assemble pre-built sections using cranes and specialized equipment, connecting utilities and finishing exterior elements. This compressed on-site timeline minimizes exposure to weather-related delays that commonly extend traditional construction schedules. The controlled factory environment also ensures consistent quality, as each component undergoes inspection before leaving the manufacturing facility. Workers specialize in specific tasks, improving efficiency and reducing errors that might require costly corrections during traditional on-site construction.
How Prefabricated Homes Help Reduce Construction Costs
Cost considerations remain central to housing decisions, and prefabricated construction offers several financial advantages. Factory production enables bulk material purchasing at reduced prices, and streamlined workflows minimize labor hours per square foot. Reduced construction timelines translate to lower financing costs, as construction loans accrue interest for shorter periods.
Cost Estimation Overview
Prices for prefabricated homes vary based on size, customization level, location, and manufacturer. The following table provides general cost estimates for different prefab home types:
| Home Type | Size Range | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Modular Home | 1,000-2,500 sq ft | $80,000-$250,000 |
| Panelized Home | 1,200-2,800 sq ft | $90,000-$280,000 |
| Manufactured Home | 800-2,000 sq ft | $50,000-$120,000 |
| Container Home | 600-1,800 sq ft | $60,000-$180,000 |
| Tiny Prefab Home | 200-600 sq ft | $30,000-$80,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
These estimates typically include the structure itself but may not cover land, foundation, site preparation, utility connections, permits, or transportation costs. Regional variations in labor rates, building codes, and land prices significantly impact total project costs. Buyers should obtain detailed quotes from multiple manufacturers and factor in all associated expenses when budgeting for a prefabricated home.
Energy Efficiency Advantages of Prefab Homes
Energy performance represents a significant long-term value proposition for prefabricated housing. Factory construction allows for precise installation of insulation materials, creating tight building envelopes that minimize air leakage. Many manufacturers incorporate advanced insulation techniques including spray foam, structural insulated panels, and continuous insulation layers that exceed standard building code requirements.
Prefab homes often feature energy-efficient windows, high-performance HVAC systems, and LED lighting as standard or easily added options. The controlled manufacturing environment ensures proper sealing around windows, doors, and penetrations, eliminating gaps that compromise energy efficiency in traditional construction. Some manufacturers design homes to meet or exceed Energy Star certification standards, resulting in lower utility bills throughout the home’s lifespan. Reduced heating and cooling demands not only decrease monthly expenses but also lower the home’s carbon footprint, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
Minimizing Construction Waste
Environmental sustainability extends beyond energy efficiency to encompass the construction process itself. Traditional on-site construction generates substantial waste, with estimates suggesting that ten to fifteen percent of building materials end up in landfills. Prefabricated construction dramatically reduces this waste through precise material ordering, optimized cutting processes, and recycling programs within manufacturing facilities.
Factory settings enable systematic waste management, with scrap materials sorted and recycled rather than discarded. Leftover lumber, metal, and other materials from one project can be repurposed for subsequent builds. Weather protection in factories prevents material damage that often results in waste at outdoor construction sites. Additionally, the ability to return unused materials to organized inventory systems reduces overordering and disposal. This waste reduction translates to environmental benefits and cost savings that can be passed to buyers. As construction industries face increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, the inherent waste reduction of prefabricated construction positions it as an environmentally responsible choice.
Prefabricated homes represent a practical intersection of affordability, efficiency, and sustainability in residential construction. As manufacturing techniques advance and design options expand, these homes continue gaining acceptance across diverse housing markets. Understanding the construction process, cost structures, and performance benefits enables prospective buyers to evaluate whether prefabricated housing aligns with their needs and values. The combination of reduced construction timelines, lower costs, superior energy performance, and minimal environmental impact makes prefab homes an increasingly relevant option in the American housing landscape.